PDPP4T, also referred as DPP4T, DPP-4T, pDPP, PDQT [CAS 1267540-03-3] is made with higher molecular weight for higher performance. For more information, please click the typical COA linked below.
Polymeric Hole Transport Materials
SWIR-OPD, benchmark PD1300T1, extremely low dark current and high detectivity
Thanksgiving release: PD1300T1, new benchmarking polymeric donor for SWIR-OPD with peak sensitivity approaches 1300nm, extremely low dark current and high detectivity.
To learn more, please click the link below:
PBOF WBG wide bandgap ST-OPV ST-OSC
PBOF: an ultrawide bandgap polymer donor with an optical band-gap to 2.20 eV. The opaque OSCs based on PBOF can afford a PCE of 15.60% in the binary device and a PCE of 16.40% in the ternary device due to the good charge transport property of the polymer and optimal active layer morphology. The EQE spectra of the PBOF-based opaque OSCs delivered a remarkable concave coverage in the visible region that matches well with the human eye photopic response spectrum. As a result, the ST-OSCs based on PBOF afforded a PCE over 10% with an AVT over 30% without optical modulation.

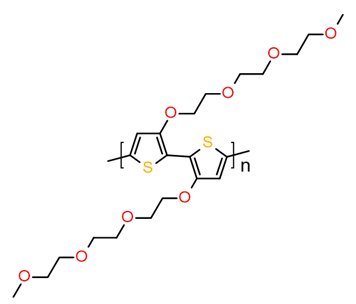
OMIEC, organic mixed ionic-electronic conductors for energy storage, electrochromic displays, bioelectronics, sensors, electrocatalysis, neuromorphic devices, thermoelectrics, and actuators
Mixed ionic-electronic conductors, also known as mixed conductors, are an increasingly important category of materials with applications in energy storage, electrochromic displays, bioelectronics, sensors, electrocatalysis, neuromorphic devices, thermoelectrics, and actuators.
Mixed conductors exhibit both ion and electron/hole conductivity, and ionic-electronic coupling (i.e., capacitance), allowing them to effectively transduce ionic signals to electronic ones, and vice versa.
In recent years, new mixed conductors have been developed beyond the traditional metals oxides and phosphates to include (semi)conducting polymers, radical polymers, perovskites, and hybrid organic-inorganic materials, enabling improved performance and new functionalities.
Structured below are examples of polymeric mixed conductors from 1-Material Inc.
PffBT4T-C9C13, PCE-12, CAS 2001095-79-8, all polymer solar cell, R2R green solvents OPV OPD donor
PffBT4T-C9C13.
CAS No:2001095-79-8
Polymer name:
Poly[(5,6-difluoro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole-4,7-diyl)-alt-(3,3′′′-di(2-nonyltridecyl)-2,2′,5′,2′′,5′′,2′′′-quaterthiophen-5,5′′′-diyl)]